News & Events
The success of the International Biofabrication Conference 2015

Category: Group Activities
In total there were 254 registered attendees, of which 81 were students. In total, 161 abstracts (including 12 abstracts from invited lectures) were submitted.
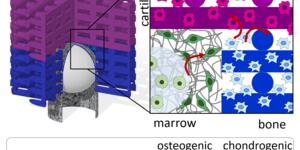
The biofabrication conference 2015 focused this year on 5 major themes, which were introduced each by a plenary speaker, and 12 parallel sessions through the 3 days of the conference that focused on major topics of importance to the community. The program was opened on Saturday 7th November 2015, with two plenary lectures from Prof. Hans Clevers and Prof. Gregory Payne, who showcased the importance of organoids and of biomimetic principles, respectively, for biofabrication strategies. While Prof. Clevers showed how organoids can be engineered with a prescribed spatial organization resulting in efficient regeneration of internal organs such as intestine and pancreas, Prof. Payne introduced a few examples in our body where mimicking electrical signals in the design of biofabricated devices resulted in enhanced tissue regeneration. On Saturday 8th November, Prof. Takeuchi showed how clinically relevant tissues can be fabricated by so called bottom-up approaches where microtissues are first formed through designed molds and then placed together through assembling techniques to create macroscopic tissue constructs. He showed a few applications where such construct hold promise for clinical translation, in particular in case of diabetic and neural diseases. On the same day, Prof. Jayasinghe discussed with a provocative lecture the most recent advanced in the field of cell electrospinning, where cellular threads can be achieved by exposing cells into an electric field of high voltage a very low current. As in any other processing technology, when cells are processed directly via the chosen technology, there is great need to characterize the safety of the process and the lack of cellular and molecular alterations to the cells themselves. Finally, on Monday 9th November, Prof. Cao illustrated several clinical cases where biologically inspired fabrication technologies have made a difference, in particular focusing on cartilage regeneration.
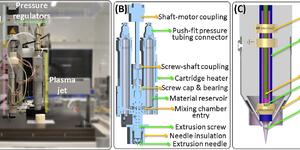
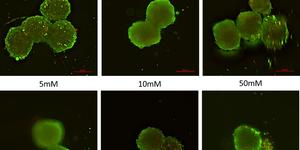
The parallel sessions were focused on topics at the heart of biofabrication: scaffold-based and scaffold-free approaches, new materials, new technologies, in vitro models, engineered tissues and organs, and bioinspired biomimetics. Each of these topics was introduced by a keynote speaker, who discussed the state of the art and introduced new advanced. In the scaffold-based biofabrication approaches session, Dr. Melchels introduced the need to expand the palette of biomaterials or bioinks used in biofabrication. Such new biomaterials should be better able to mimic what native biomaterials in our tissues and organs, for example by obtaining in combination with processing technologies better resolution of the fabricated features or by allowing better interactions at the interface with cells. This need was further elaborated by Prof. Groll in the new materials session, who introduced the a few novel chemistries, including block-copolymers and supramolecular chemistries that have the potential to do so. In addition, Dr. Gillner introduced new technologies able to obtain micron scaled resolution thanks to the exploitation of photonic principles, which was presented in the new technologies session. In Scaffold-free biofabrication approaches session, Prof. Nakayama introduced a spheroid automated dispensing technology with which large scale tissues could be produced and showed intriguing applications for skeletal regeneration. With a similar approach, Prof. Mironov surprised the community showing the first attempt to print a gland, specifically a thyroid, and announced the first set of preclinical tests to be starting by the beginning of next year. In the in vitro models session, Prof. Yoo showed the potential of bioprinting technologies to create 3D models that are better representative for pharmaceutical studies than classical 2D cultures. Finally, in the bioinspired biomimetics session, Prof. Truekcenmuller introduced new micro-objects that could be used in combination with the bottom-up approaches introduced by Prof. Tekeuchi to create clinically relevant large constructs where the micro-objects can also impart cells specific functionalities.